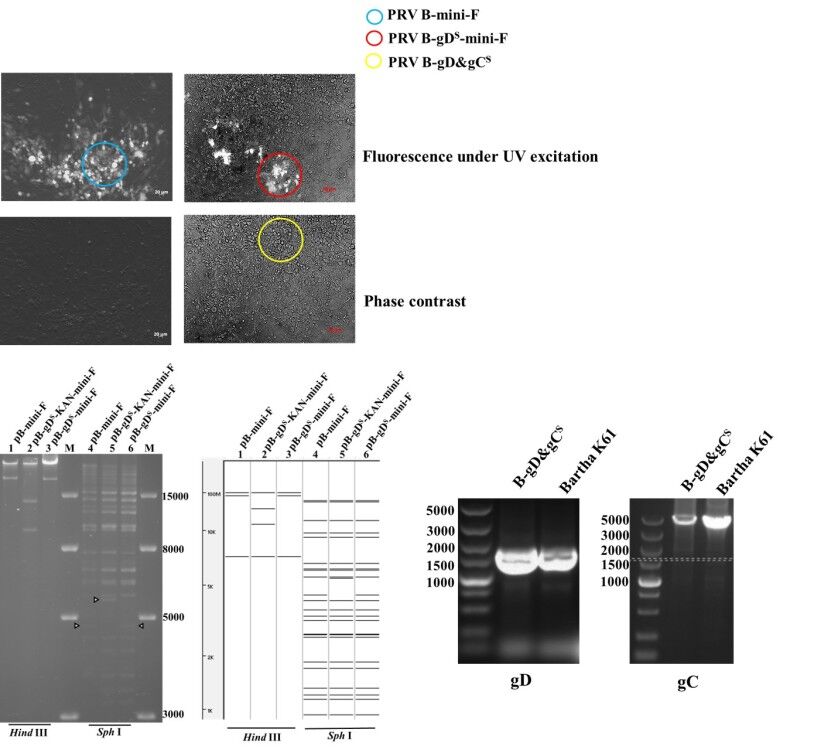
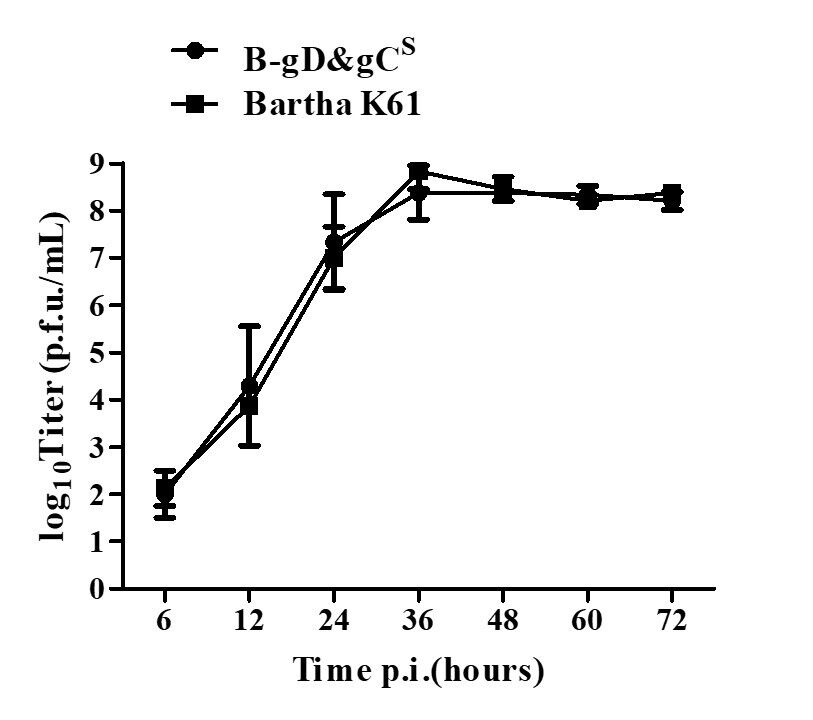
We described the construction of a gD&gC-substituted pseudorabies virus (PRV B-gD&gCS) from the Bartha-K61 (as backbone) and AH02LA strain (as template for gD and gC genes) through BAC technology using homologous recombination. The growth kinetics of PRV B-gD&gCS was compared with Bartha-K61. Its safety was evaluated in 28-day-old piglets. Protection efficacy was tested in piglets by lethal challenge with AH02LA at 7 days post vaccination, including body temperature, clinical symptoms, virus shedding, mortality rate, and lung lesions. The results showed that a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone of Bartha K61 BAC and a gD&gC-substituted pseudorabies virus (PRV B-gD&gCS) were generated. The growth kinetics of PRV B-gD&gCS strain on ST (Swine testicular) cell was similar to that of the Bartha-K61 strain. All piglets inoculated intramuscularly with PRV B-gD&gCS strain did not exhibit any clinical symptoms and virus shedding. After AH02LA challenge, all piglets in PRV B-gD&gCS and Bartha-K61 group survived without exhibiting any clinical symptoms and high body temperature. Moreover, piglets in PRV B-gD&gCS group improved effectively virus shedding post challenge compared with piglets in Bartha K61 group. Our results suggest that PRV B-gD&gCS strain is a promising vaccine candidate for the effective control of current severe epidemic pseudorabies in China.