SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) which is abundant and dispersed widely in the genome is suitable for large-scale and automated genotyping. In this study, highly polymorphic bi-allelic SNP loci were screened and 700 KASP (Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR) molecular markers were developed based on resequencing data of 205 diverse maize inbred lines. Among them, 202 KASP markers validated by 46 representative lines were further used for phylogenetic tree construction and genetic structure analysis. The validated KASP markers distributed evenly on 10 chromosomes in maize with an average PIC of 0.463 and an average MAF of 0.451. The phylogenetic tree constructed by KASP markers is highly consistent with that by re-sequencing data. In addition, the genetic similarity coefficient evaluated between KASP loci and the total SNP loci achieved 89.5% which demonstrated the availability of KASP in heterotic group division. These findings suggest that 202 KASP markers play an important role in analysis of germplasm resource, construction of genetic map, and division of heterotic group in maize.
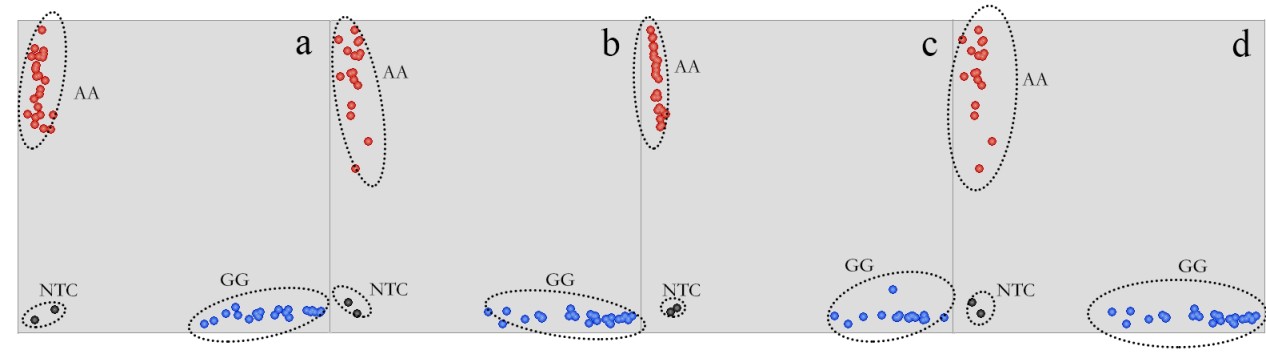
Genotyping map of KASP markers


